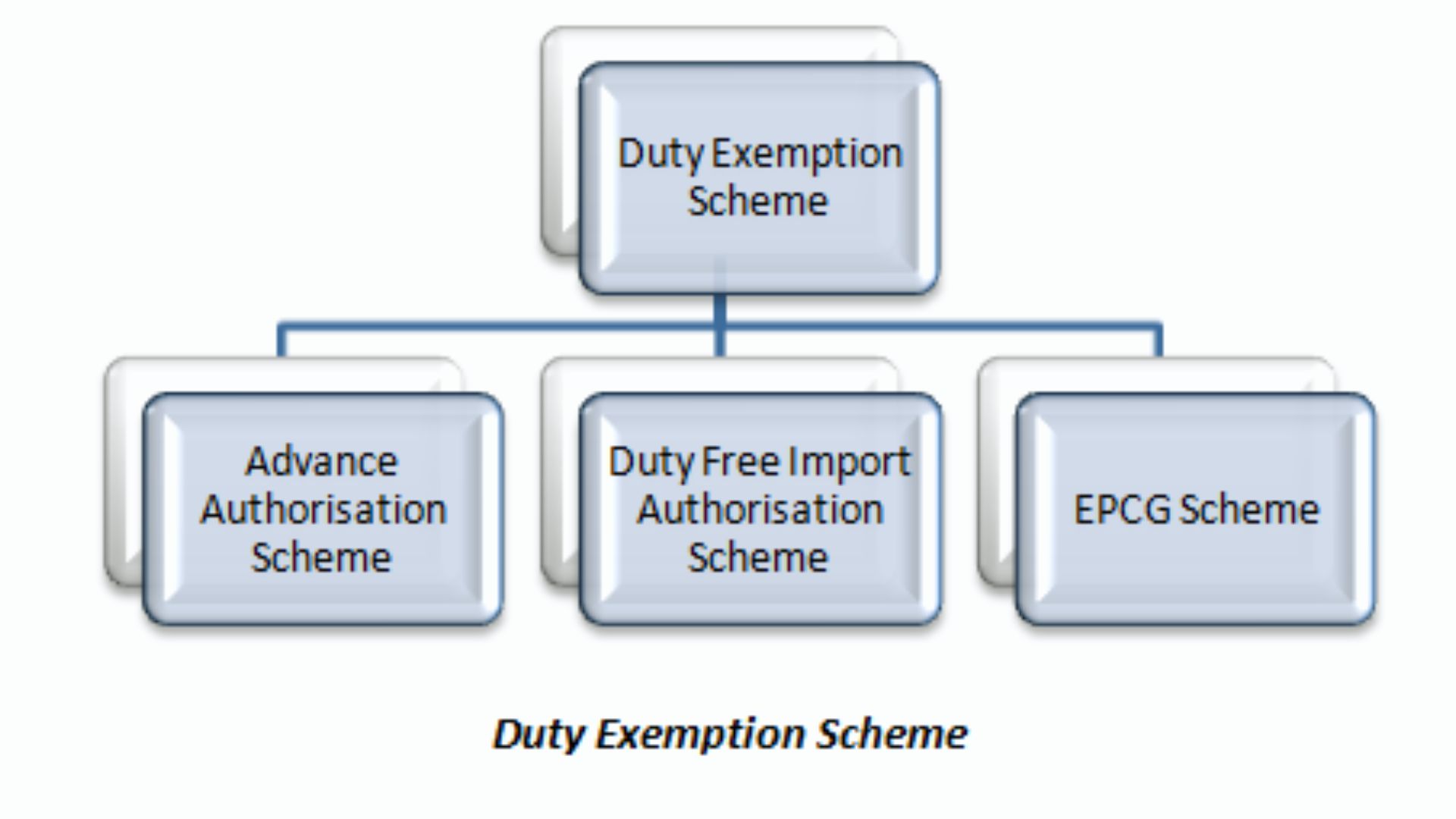
Duty exemption schemes
Duty exemption schemes are instrumental mechanisms implemented by governments to encourage and facilitate international trade by providing relief from import duties and taxes on specific goods or commodities. These schemes aim to stimulate exports, promote domestic production, and attract foreign investment by reducing the cost of importing raw materials, components, or capital goods necessary for manufacturing or processing export-oriented products. Duty exemption schemes typically involve the issuance of certificates or licenses to eligible businesses, allowing them to import specified goods duty-free or at reduced rates, subject to certain conditions and export obligations.

One prominent example of a duty exemption scheme is the Duty-Free Import Authorization (DFIA) scheme in India, which allows exporters to import inputs for the manufacture of export products without paying customs duties. Under the DFIA scheme, exporters are required to fulfill specified export obligations within a prescribed time frame, typically through the export of finished goods manufactured using the imported inputs. By providing duty exemptions on imported inputs, the DFIA scheme helps reduce production costs for exporters, enhance their competitiveness in international markets, and promote value addition within the country.
Moreover, duty exemption schemes play a crucial role in facilitating trade and investment by creating a conducive environment for businesses to operate and expand their operations. By reducing trade barriers and compliance costs associated with import duties and taxes, these schemes encourage businesses to invest in new ventures, expand production capacities, and explore new markets. Additionally, duty exemption schemes contribute to the diversification of exports, the development of strategic industries, and the overall economic growth and development of countries by promoting innovation, competitiveness, and entrepreneurship in the global marketplace.